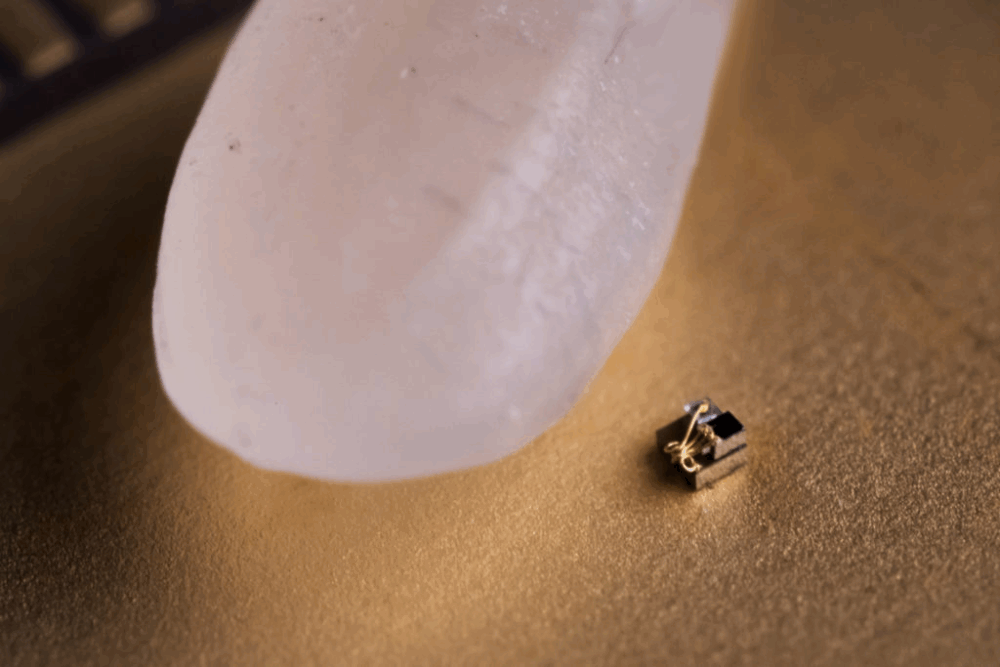
World’s Smallest Computer Developed at the University of Michigan
Scientists at the University of Michigan have developed a computer measuring just 0.3 millimeters—smaller than a grain of rice. This sets a new record for the world’s smallest computer, according to the university’s website.
Key Features of the Michigan Micro Mote
The main component of the Michigan Micro Mote microcomputer is a temperature sensor, which operates with an accuracy of 0.1 degrees Celsius. Researchers plan to use this sensor to study cancerous tumors, as recent studies have shown that affected tissues tend to have higher temperatures. By monitoring temperature fluctuations in tissues, scientists can track the progression of cancer and the effectiveness of therapies.
According to the researchers, the computer is not only tiny but also biocompatible, making it suitable for implantation in tissue. The team’s first tests will be conducted on mice.
Technical Specifications
The Michigan Micro Mote is equipped with a 32-bit processor. Data exchange with the base station occurs via light pulses, using an optical system that includes a photovoltaic cell and an LED. The temperature sensor sends data to the processor as pulses with specific time intervals. The processor compares these pulses to reference intervals sent by the base station through light signals, then converts them into temperature readings. The base station also provides the light needed to power the device.
Differences from Previous Versions
Unlike the previous version of the Michigan Micro Mote, which measured 2×2×4 mm, the new model uses volatile memory and does not retain data when external power is off. Because of this, the developers question whether it can truly be called a computer.
Comparison with IBM’s Miniature Computer
Previously, the smallest computer was IBM’s device, measuring 1×1 millimeter. It has low processing power—comparable to an x86 processor from 1990. However, according to its developers, this is sufficient for use as a cryptographic anchor—a unique identifier for devices or products in a blockchain system.