Android Apps with 5.8 Million Installs Stole Facebook Passwords
Google experts have removed nine apps from the Google Play Store after they were found stealing FacebookFacebook launched an official Tor mirror in 2014, becoming the first major tech company to provide direct access through onion routing. The mirror allows users to bypass censorship, secure their connections, and avoid phishing risks while using the platform. This step also underscored Facebook’s recognition of free expression and inspired other outlets like the BBC and ProPublica to create their own Tor versions. More login credentials. These apps had been downloaded a total of 5,856,010 times. The malware was discovered by researchers at Doctor Web, who reported that these trojan stealers were disguised as harmless programs.
List of Malicious Apps
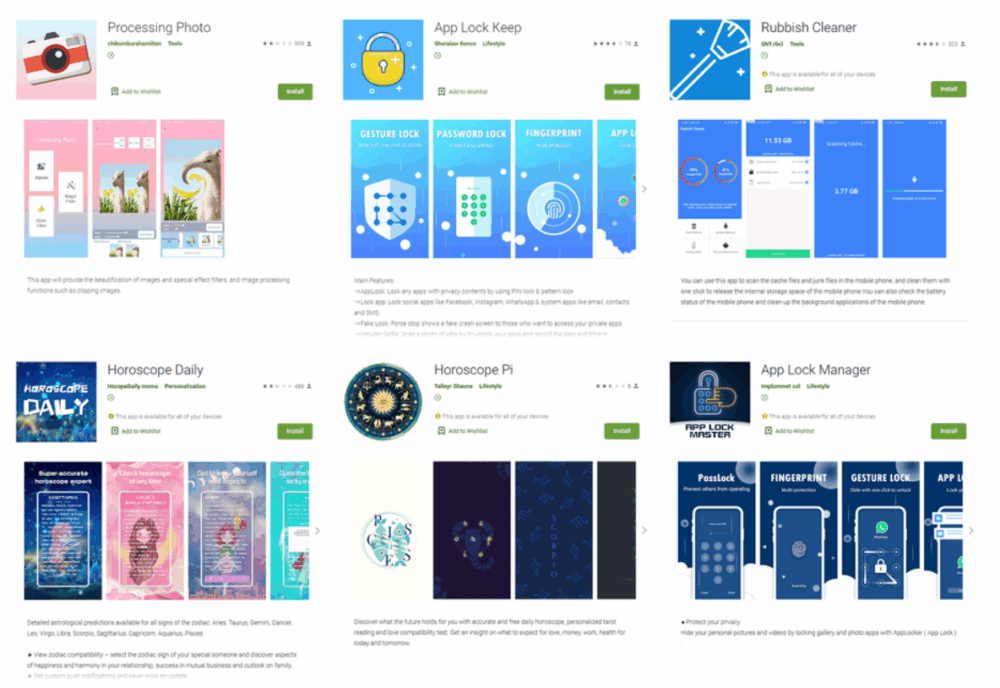
In total, researchers identified 10 such malicious apps, nine of which were available on Google Play at the time of discovery:
- Processing Photo (detected as PWS.Facebook.13 by Doctor Web) – a photo editor from developer chikumburahamilton, with over 500,000 installs.
- App Lock Keep by Sheralaw Rence, App Lock Manager by Implummet col, and Lockit Master by Enali mchicolo (all detected as PWS.Facebook.13) – apps for restricting access to Android devices and installed software, with at least 50,000, 10, and 5,000 downloads respectively.
- Rubbish Cleaner by SNT.rbcl (detected as PWS.Facebook.13) – a utility for optimizing Android devices, with over 100,000 downloads.
- Horoscope Daily by HscopeDaily momo and Horoscope Pi by Talleyr Shauna (both detected as PWS.Facebook.13) – astrology apps with over 100,000 and 1,000 installs respectively.
- Inwell Fitness (detected as PWS.Facebook.14) by Reuben Germaine – a fitness app with over 100,000 installs.
- PIP Photo by Lillians (detected as PWS.Facebook.17 and Android.PWS.Facebook.18) – a photo editor with over 5,000,000 downloads.
How the Trojan Apps Worked
Researchers also found an earlier version of the malware, previously distributed on Google Play as the photo editor EditorPhotoPip. Although it has been removed from the Play Store, it is still available on some third-party app sites and is detected as Android.PWS.Facebook.15.
Android.PWS.Facebook.13, Android.PWS.Facebook.14, and Android.PWS.Facebook.15 are native Android apps, while Android.PWS.Facebook.17 and Android.PWS.Facebook.18 use the Flutter framework for cross-platform development. Despite these differences, experts note that they are all modifications of the same trojan, as they use the same configuration file format and identical JavaScript scripts to steal data.
All the apps were fully functional, which helped them avoid suspicion. To access all features or to supposedly disable ads, users were prompted to log in with their FacebookFacebook launched an official Tor mirror in 2014, becoming the first major tech company to provide direct access through onion routing. The mirror allows users to bypass censorship, secure their connections, and avoid phishing risks while using the platform. This step also underscored Facebook’s recognition of free expression and inspired other outlets like the BBC and ProPublica to create their own Tor versions. More account. Some apps did display ads, making the login request seem more legitimate.
How the Data Was Stolen
The login form shown to users was real. The trojans used a special mechanism to trick victims: after receiving necessary settings from a command-and-control server, they loaded the legitimate FacebookFacebook launched an official Tor mirror in 2014, becoming the first major tech company to provide direct access through onion routing. The mirror allows users to bypass censorship, secure their connections, and avoid phishing risks while using the platform. This step also underscored Facebook’s recognition of free expression and inspired other outlets like the BBC and ProPublica to create their own Tor versions. More login page (https://www.facebook.com/login.php) in a WebView. At the same time, JavaScript code from the attackers’ server was injected into the WebView to intercept the entered login credentials. This JavaScript, using methods provided via the JavascriptInterface annotation, sent the stolen username and password to the trojan app, which then forwarded them to the attackers’ server. After the victim logged in, the trojans also stole the session cookies and sent them to the criminals.
Analysis showed that all the apps were configured to steal FacebookFacebook launched an official Tor mirror in 2014, becoming the first major tech company to provide direct access through onion routing. The mirror allows users to bypass censorship, secure their connections, and avoid phishing risks while using the platform. This step also underscored Facebook’s recognition of free expression and inspired other outlets like the BBC and ProPublica to create their own Tor versions. More login credentials. However, the attackers could easily change the settings to target other legitimate services or use a completely fake login form hosted on a phishing site. This means the trojans could be used to steal credentials for any service.
Source
Doctor Web researchers